A Safety Data Sheet (SDS), also known as a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), is a detailed document that provides information about the potential hazards and safe handling of a chemical substance or product. The format and content of an SDS are standardized and regulated by various agencies worldwide, such as OSHA in the United States, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS).
One of the key elements of an SDS is the table of contents, which provides a roadmap to the various sections and subsections of the document. The table of contents helps users quickly locate the specific information they need, whether they are looking for details on hazards, handling precautions, or first aid measures. A well-structured table of contents is essential for ensuring that the SDS is both user-friendly and compliant with regulations.
Essential Sections of an SDS Table of Contents
The content and organization of an SDS table of contents may vary slightly depending on the specific regulations and standards being followed. However, there are several essential sections that are typically included:
- Section 1: Identification: Provides basic information about the substance or product, including its name, chemical identity, manufacturer or supplier details, and recommended uses.
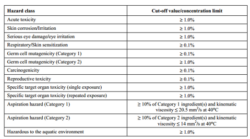
- Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification: Classifies the potential hazards of the substance or product according to standardized criteria, such as flammability, toxicity, and environmental hazards.
- Section 3: Composition/Information on Ingredients: Lists the chemical components of the substance or product, including their concentrations and any hazardous ingredients.
- Section 4: First-Aid Measures: Provides instructions on what to do in case of accidental ingestion, inhalation, skin contact, or eye contact with the substance or product.
- Section 5: Fire-Fighting Measures: Outlines the appropriate fire-fighting techniques and extinguishing agents for the substance or product, as well as any special hazards firefighters may face.
- Section 6: Accidental Release Measures: Provides guidance on how to safely clean up and dispose of spilled or leaked material, minimizing environmental and health risks.
- Section 7: Handling and Storage: Describes the proper procedures for handling and storing the substance or product to prevent accidents and maintain its stability.
- Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection: Recommends appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and engineering controls to protect workers from exposure to hazardous substances.
- Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties: Lists the physical and chemical properties of the substance or product, such as appearance, boiling point, flash point, and pH.
- Section 10: Stability and Reactivity: Provides information on the stability and reactivity of the substance or product, including incompatible materials and conditions to avoid.
- Section 11: Toxicological Information: Summarizes the toxicological data on the substance or product, including potential health effects and routes of exposure.
- Section 12: Ecological Information: Assesses the potential environmental impacts of the substance or product, including its effects on aquatic life, soil, and vegetation.
- Section 13: Disposal Considerations: Provides instructions on how to properly dispose of the substance or product and any contaminated materials.
- Section 14: Transport Information: Provides information on the safe transport of the substance or product, including shipping regulations and special precautions.
- Section 15: Regulatory Information: Lists the applicable regulations and compliance information for the substance or product, such as hazard classification and risk phrases.
- Section 16: Other Information: Includes any additional information or references that may not fit into the other sections, such as preparation date, revision history, and references to data sources.
Using a Template to Create an SDS Table of Contents
To ensure that your SDS table of contents is comprehensive and compliant with regulations, it is recommended to use a template that has been designed specifically for this purpose. There are many free and paid templates available online from government agencies, industry organizations, and software providers. These templates typically include all the necessary sections outlined above and provide a consistent structure for organizing the information.
By using a safety data sheet table of contents template, you can save time and effort in creating your SDS and ensure that it meets the required standards.