A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are anything that the company owns, such as cash, inventory, and equipment. Liabilities are anything that the company owes, such as accounts payable, loans, and taxes. Equity is the difference between the company’s assets and liabilities. A balance sheet is essential for any business, as it can be used to track the company’s financial progress and make informed decisions about the future.
For start-up businesses, a balance sheet is especially important. It can help the company to raise funding, as it shows investors the company’s financial health and stability. A balance sheet can also help the company to track its progress and identify areas where it needs to improve.
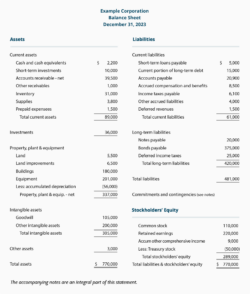
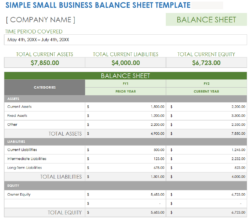
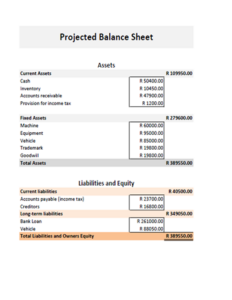
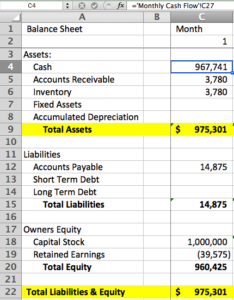
There are many different ways to format a balance sheet. However, the most common format is the T-account format. In this format, the assets are listed on the left side of the T-account, and the liabilities and equity are listed on the right side. The total assets must always equal the total liabilities plus equity. To use the **start up business balance sheet template**, you need to have all the details of company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Once your details are ready, you need to fill relevant information in the template. Always use a specific date as the snapshot in the balance sheet because it is important to note that a balance sheet is only a snapshot of the company’s financial health on a particular date. The company’s financial health can change significantly over time, so it is important to review the balance sheet regularly.
Assets
Assets are anything that the company owns. They can be divided into two main categories: current assets and non-current assets. Current assets are assets that can be easily converted into cash, such as cash, inventory, and accounts receivable. Non-current assets are assets that cannot be easily converted into cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment. Assets are essential for any business, as they allow the company to operate and generate revenue.
When preparing a balance sheet, it is important to list the assets in order of liquidity. Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be converted into cash. The most liquid assets should be listed first, followed by the less liquid assets. This will help you to get a clear picture of the company’s financial health.
It is also important to note that assets are recorded on the balance sheet at their historical cost. This means that the cost of the asset when it was purchased is used to determine its value on the balance sheet. However, the fair market value of the asset may be different from its historical cost. The fair market value is the price that the asset would sell for on the open market.
Finally, it is important to remember that assets are not always what they seem. For example, a company may have a large amount of inventory on its balance sheet. However, if the inventory is obsolete or damaged, it may not be worth as much as the company thinks it is. It is important to carefully evaluate the value of the company’s assets before making any decisions about the company’s financial health.
Liabilities
Liabilities are anything that the company owes. They can be divided into two main categories: current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are liabilities that are due within one year, such as accounts payable, loans, and taxes. Non-current liabilities are liabilities that are not due within one year, such as bonds and mortgages.
Liabilities are essential for any business, as they allow the company to finance its operations. However, too much debt can be a burden on the company and can lead to financial distress. It is important to carefully manage the company’s liabilities and ensure that the company has enough cash flow to meet its obligations.
When preparing a balance sheet, it is important to list the liabilities in order of maturity. Maturity refers to the date when the liability is due. The liabilities that are due first should be listed first, followed by the liabilities that are due later. This will help you to get a clear picture of the company’s financial health.
It is also important to note that liabilities are recorded on the balance sheet at their present value. This means that the amount of the liability that is still owed is used to determine its value on the balance sheet. The present value of a liability is the amount of money that would be required to pay off the liability today.
Finally, it is important to remember that liabilities are not always what they seem. For example, a company may have a large amount of debt on its balance sheet. However, if the company has a strong cash flow and is able to make its payments on time, the debt may not be as burdensome as it seems. It is important to carefully evaluate the company’s liabilities before making any decisions about the company’s financial health.
A balance sheet is an essential financial statement for any business. It can be used to track the company’s financial progress and make informed decisions about the future. By understanding the different components of a balance sheet, you can get a clear picture of the company’s financial health and make informed decisions about the company’s future.
There are many different ways to use a balance sheet. For example, a balance sheet can be used to:
- Track the company’s financial progress over time
- Identify areas where the company needs to improve
- Make informed decisions about the company’s future
A balance sheet is a valuable tool for any business. By understanding how to use a balance sheet, you can make informed decisions about the company’s financial future.