A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. A micro entity balance sheet template is a simplified version of a balance sheet that is designed for small businesses.
There are many different micro entity balance sheet templates available online. You can find templates from accounting software providers, banks, and other financial institutions. Once you have found a template, you can customize it to fit your business’s needs.
When creating your micro entity balance sheet, it is important to include all of your assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are anything that your business owns, such as cash, inventory, and equipment. Liabilities are anything that your business owes, such as accounts payable and loans. Equity is the difference between your assets and your liabilities.
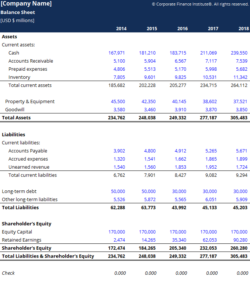
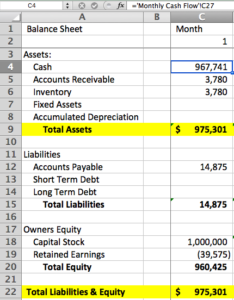
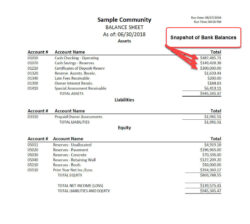
Assets
Assets are listed on the left side of the balance sheet. They are typically divided into two categories: current assets and non-current assets. Current assets are assets that can be easily converted into cash, such as cash, inventory, and accounts receivable. Non-current assets are assets that cannot be easily converted into cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment.
When listing your assets, it is important to include their current market value. This will give you a better understanding of your company’s financial health.
One important aspect of assets is that they can be classified into tangible and intangible assets. Tangible assets are physical assets that can be seen and touched, such as buildings, inventory, and equipment. Intangible assets, on the other hand, are non-physical assets that do not have a physical form, such as patents, trademarks, and goodwill.
When preparing a micro entity balance sheet, it is essential to accurately represent the value of assets. This involves considering factors such as depreciation and amortization, which reduce the value of assets over time due to usage or obsolescence.
Finally, it’s worth noting that assets are a crucial component of a micro entity’s financial health. By effectively managing and optimizing its assets, a micro entity can improve its overall financial stability and growth potential.
Liabilities
Liabilities are listed on the right side of the balance sheet. They are typically divided into two categories: current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are liabilities that will come due within one year, such as accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses. Non-current liabilities are liabilities that will not come due within one year, such as long-term loans and mortgages.
When listing your liabilities, it is important to include the interest rate and maturity date for each liability. This will help you understand the cost of your debt and when it will be due.
Just like assets, liabilities can also be categorized as current and non-current. Current liabilities are short-term obligations that are due within a year, such as accounts payable, taxes payable, and short-term loans. Non-current liabilities, on the other hand, are long-term obligations that extend beyond a year, such as long-term loans, bonds, and mortgages.
Properly managing liabilities is crucial for a micro entity’s financial stability. By effectively meeting its obligations and liabilities, a micro entity can maintain a positive reputation with creditors and lenders, which can lead to better financing opportunities and reduced borrowing costs.
Conclusion
A micro entity balance sheet template can be a helpful tool for small businesses. It can help you track your assets, liabilities, and equity, and make informed financial decisions. By understanding your company’s financial health, you can make better decisions about how to allocate your resources and grow your business.