An insurance agency balance sheet template is an essential tool for agencies looking to track their financial health and ensure compliance with industry regulations. It provides a snapshot of the agency’s assets, liabilities, and equity, allowing them to assess their financial performance and make informed decisions.
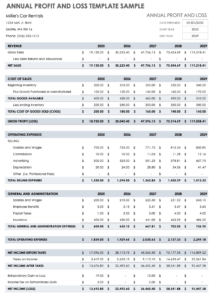
Insurance agencies often have complex financial structures due to the nature of their business. They collect premiums from policyholders, pay claims, and invest in various assets. An accurate balance sheet helps agencies manage these complexities, ensuring that they have sufficient capital to meet their obligations and pursue growth opportunities.
In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to using an insurance agency balance sheet template, including its key components and how to interpret the information it provides. We will also discuss the importance of maintaining accurate financial records and how to use this template to enhance your agency’s financial performance.
Understanding the Insurance Agency Balance Sheet
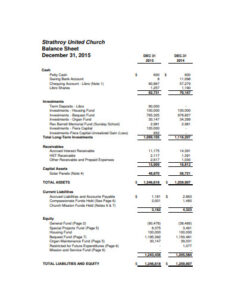
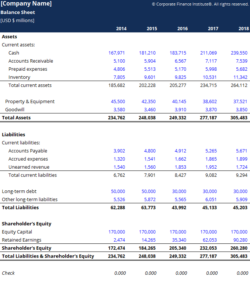
An insurance agency balance sheet is divided into three main sections: assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets represent the resources owned by the agency, such as cash, investments, and accounts receivable. Liabilities represent the amounts owed by the agency, such as outstanding claims, unearned premiums, and taxes payable.
Equity is the residual interest in the agency’s assets after subtracting its liabilities. It represents the ownership stake of the agency’s owners. By understanding the relationship between these three components, insurance agencies can assess their financial stability and make informed decisions.
Assets are typically listed in order of liquidity, with cash and cash equivalents being the most liquid assets. Liabilities are presented in order of maturity, with current liabilities being due within a year and long-term liabilities maturing at a later date.
Equity may include various components, such as contributed capital, retained earnings, and undistributed earnings. Contributed capital represents the amount invested by the agency’s owners, while retained earnings represent the accumulated profits that have been reinvested in the business.
Undistributed earnings are profits that have not yet been distributed to owners. Equity serves as a buffer against losses and provides a basis for measuring the agency’s financial leverage.
Using the Insurance Agency Balance Sheet Template
Using an insurance agency balance sheet template is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. The template should be tailored to the specific needs of your agency, considering the size and complexity of your operations.
When completing the balance sheet, it is important to use accurate and up-to-date information. This includes recording all assets, liabilities, and equity at their fair market value. Failure to do so can result in misleading financial statements.
Once the balance sheet is complete, it should be reviewed and analyzed regularly. This will help you identify trends, evaluate financial risks, and make informed decisions about your agency’s operations. By regularly monitoring your balance sheet, you can ensure that your agency remains financially healthy and on track to achieve its goals.
Conclusion
An insurance agency balance sheet template is an invaluable tool for managing the financial health of an agency. By providing a snapshot of the agency’s assets, liabilities, and equity, it allows agencies to assess their financial performance, make informed decisions, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Maintaining accurate financial records is essential for using the balance sheet template effectively. Regularly reviewing and analyzing your balance sheet will help you identify trends, evaluate financial risks, and make informed decisions about your agency’s operations. By leveraging the information provided by the balance sheet, you can enhance your agency’s financial performance and achieve long-term success.