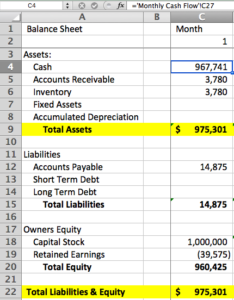
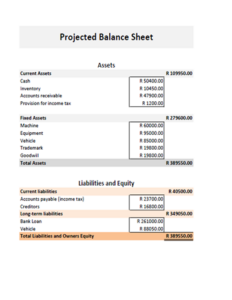
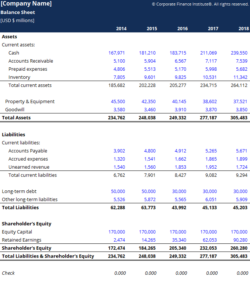
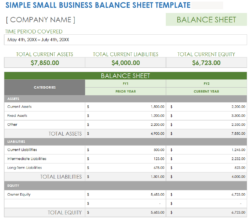
A balance sheet is a financial statement that summarizes a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. A balance sheet for a service company will typically include the following sections:
Assets: This section lists the company’s assets, which are anything that the company owns or has value. Assets are typically divided into current assets and non-current assets. Current assets are those that can be converted into cash within one year, while non-current assets are those that cannot be converted into cash within one year.
Liabilities: This section lists the company’s liabilities, which are anything that the company owes. Liabilities are typically divided into current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are those that are due within one year, while non-current liabilities are those that are not due within one year.
Assets
Assets are typically divided into two main categories: current assets and non-current assets.
Current assets are those that can be converted into cash within one year. These assets include cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
Non-current assets are those that cannot be converted into cash within one year. These assets include property, plant, and equipment, and intangible assets such as goodwill and patents.
The total value of the company’s assets is equal to the sum of its current assets and non-current assets.
The value of each asset is based on its historical cost or its fair market value. Historical cost is the price that the company originally paid for the asset. Fair market value is the current price that the asset would sell for in the market.
The value of each asset is also affected by depreciation and amortization. Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of a fixed asset over its useful life. Amortization is the process of allocating the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life.
Liabilities
Equity
Equity is the residual interest in the assets of a company after all of its liabilities have been paid. Equity is owned by the company’s shareholders.
The value of equity is equal to the difference between the company’s total assets and its total liabilities.
The value of equity can be positive or negative. If the value of equity is positive, the company has a net worth. If the value of equity is negative, the company has a deficit.
The balance sheet is a valuable tool for understanding a company’s financial health. It can be used to assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and profitability.