Navigating the financial complexities of a business can be daunting, but understanding the fundamentals is crucial for informed decision-making. Key to this understanding are the profit and loss statement and balance sheet, two essential financial statements that provide a snapshot of a company’s financial performance and health. These statements are invaluable tools for evaluating profitability, liquidity, and overall financial stability.
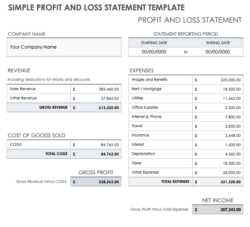
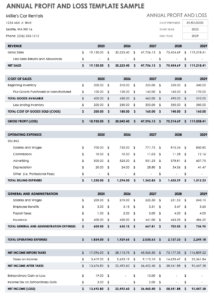
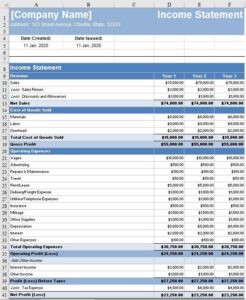
A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement, presents a summary of a company’s revenues, expenses, and profits over a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. It provides insights into the company’s ability to generate revenue, control costs, and ultimately generate profit.
On the other hand, a balance sheet offers a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It provides a comprehensive overview of the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, allowing stakeholders to assess its financial strength and solvency. Together, the profit and loss statement and balance sheet provide a comprehensive picture of a company’s financial performance and health.
Understanding the Profit and Loss Statement
The profit and loss statement is a dynamic document that captures the financial performance of a company over a specific period. It is divided into three main sections: revenue, expenses, and net income. Revenue represents the total income generated by the company from its core operations, such as sales of goods or services. Expenses, on the other hand, are the various costs incurred by the company in generating revenue, including costs of goods sold, operating expenses, and depreciation.
The difference between revenue and expenses determines the company’s net income, which is a measure of its profitability. Additionally, the profit and loss statement can be used to calculate financial ratios, such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and operating profit margin, which provide insights into the company’s financial efficiency.
Net income can be positive (profit) or negative (loss), and it significantly impacts a company’s financial position. A positive net income indicates that the company’s revenues exceed its expenses, resulting in a profit. Conversely, a negative net income signifies that the company has incurred a loss due to expenses exceeding revenue.
The profit and loss statement is a vital tool for assessing a company’s profitability, making it essential for investors, creditors, and management to evaluate the company’s financial performance and make informed decisions.
Additionally, the profit and loss statement can be used to identify areas of strength and weakness within the company’s operations. By analyzing the components of revenue and expenses, management can pinpoint opportunities for growth and areas that require improvement.
Interpreting the Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, typically the end of a reporting period. It is divided into two main sections: assets and liabilities and equity.
Assets represent the resources owned by the company, such as cash, inventory, and property. Liabilities, on the other hand, are the company’s obligations to other entities, including accounts payable, loans, and taxes. Equity, also known as net worth, represents the residual interest in the company after liabilities have been deducted from assets.
The balance sheet must always balance, meaning that the total assets must equal the sum of liabilities and equity. This equation ensures that all of the company’s resources are accounted for and that the value of its assets is equal to the sum of its obligations and ownership claims.
The balance sheet is a crucial tool for assessing a company’s financial health and solvency. By analyzing the composition of assets, liabilities, and equity, stakeholders can gain insights into the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability.
A strong balance sheet indicates that a company has sufficient assets to cover its liabilities and obligations. It also suggests that the company has a strong financial foundation and is well-positioned for growth and expansion.
By understanding both the profit and loss statement and balance sheet, stakeholders can gain a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance and health. These statements are essential tools for making informed decisions, whether it be investment, lending, or strategic planning.