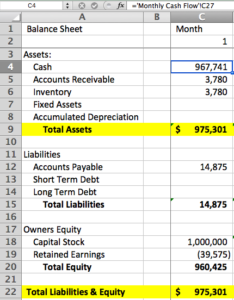
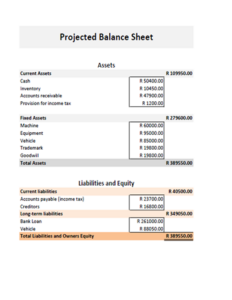
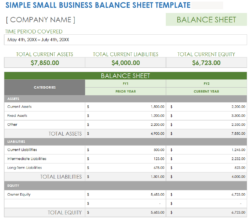
A balance sheet is a financial statement that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial health at a specific point in time. It shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets are anything that the company owns or is owed to it, such as cash, inventory, and accounts receivable. Liabilities are anything that the company owes to others, such as accounts payable, loans, and taxes. Equity is the difference between the company’s assets and liabilities. A balance sheet is important because it provides a basis for comparison with other companies, as well as for tracking the company’s financial performance over time. It also provides information about the company’s liquidity, solvency, and profitability. A well-structured balance sheet can also help you make better financial decisions.
There are many different ways to create a balance sheet. One way is to use a fill in balance sheet template. These templates are available online and can be customized to fit your specific needs. Fill in balance sheet templates typically include the following sections:
Assets
Assets are anything that the company owns or is owed to it. Assets are typically divided into two categories: current assets and non-current assets. Current assets are assets that can be easily converted into cash, such as cash, inventory, and accounts receivable. Non-current assets are assets that cannot be easily converted into cash, such as property, plant, and equipment. It is important to understand that assets are valued at their original cost less any depreciation. Depreciation is the process of spreading the cost of an asset over its useful life. This is important because it ensures that the asset is not overvalued on the balance sheet.
Examples of assets include:
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Inventory
- Accounts receivable
- Prepaid expenses
- Property, plant, and equipment
- Investments
- Intangible assets
Liabilities
Liabilities are anything that the company owes to others. Liabilities are typically divided into two categories: current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are liabilities that are due within one year, such as accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses. Non-current liabilities are liabilities that are due more than one year from now, such as long-term loans and bonds payable. Examples of liabilities include:
- Accounts payable
- Short-term loans
- Accrued expenses
- Long-term loans
- Bonds payable
- Deferred income taxes
Equity
Equity is the difference between the company’s assets and liabilities. Equity represents the ownership interest in the company. Equity can be divided into two categories: common stock and retained earnings. Common stock is the most common type of equity. It represents the ownership interest in the company that is held by the shareholders. Retained earnings are the earnings that the company has reinvested in the business. Examples of equity include:
- Common stock
- Retained earnings
- Treasury stock
- Other equity
A balance sheet is a valuable tool for understanding a company’s financial health. By using a fill in balance sheet template, you can easily create a balance sheet that meets your specific needs.